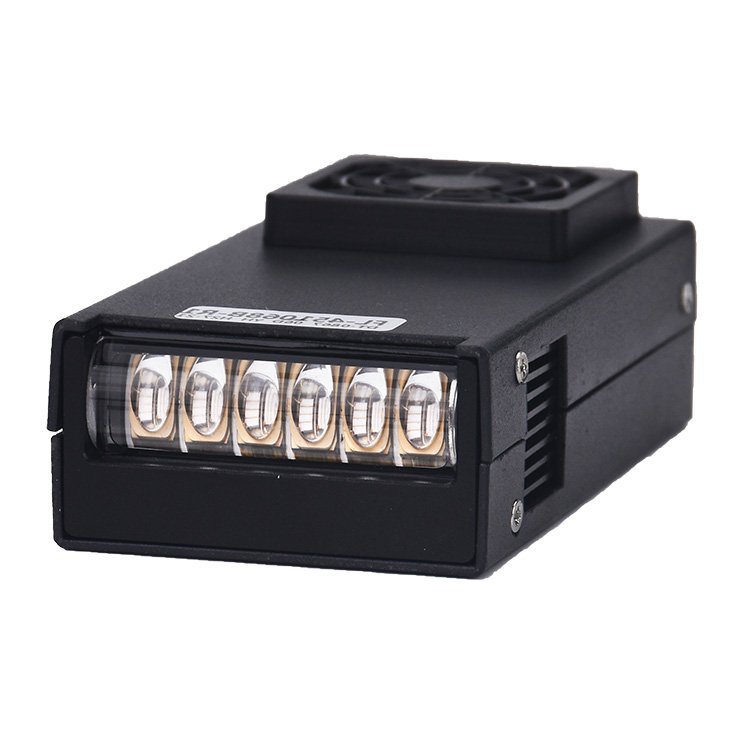
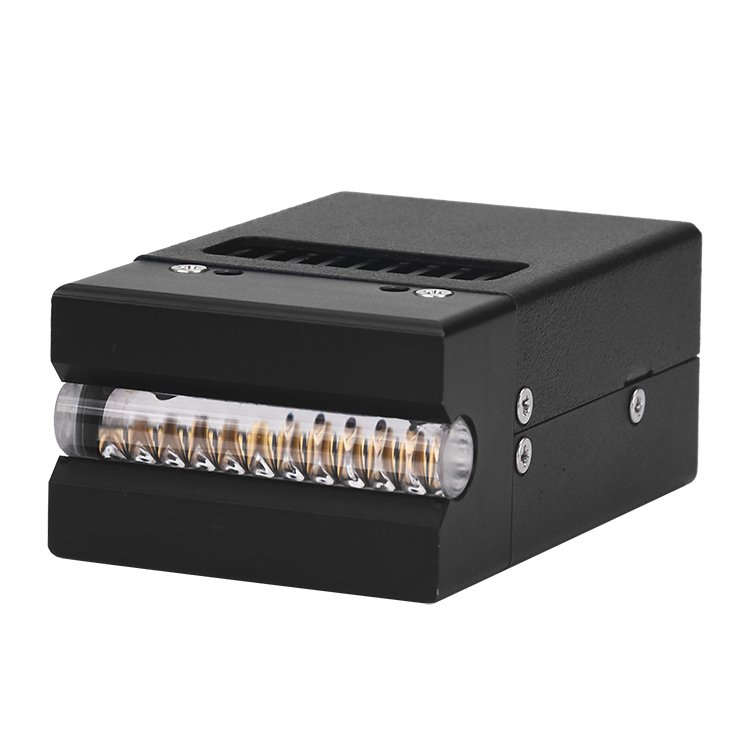
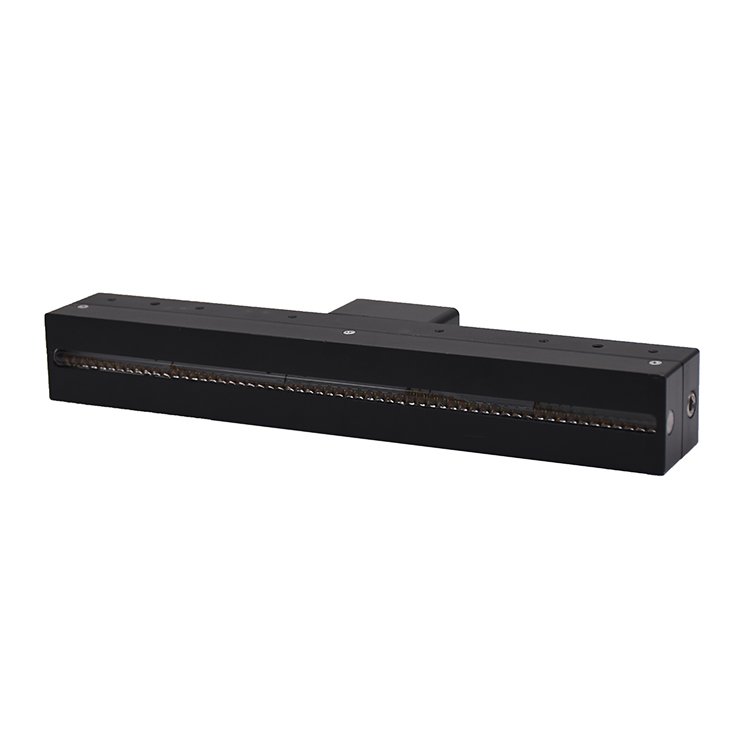
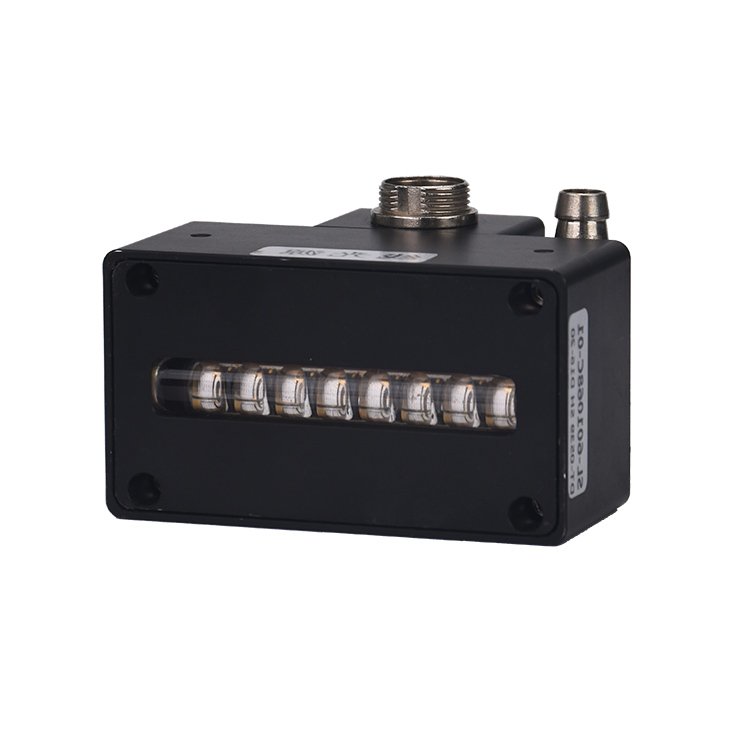
What are the characteristics of uvled? Introduction to uvled curingread count [570] release time:2021-11-26 09:11:00
With the maturity of UVLED curing technology, the fields of application have gradually begun to expand, and many industries that originally used mercury light sources have begun to be replaced by UVLED light sources. UVLED is a type of light-emitting diode. Light-emitting diodes can efficiently convert electrical energy into light energy. Compared with traditional UV mercury lamps, they are more environmentally friendly, efficient and have low energy consumption. They are currently one of the green industrial technologies that are truly oriented towards sustainable development.
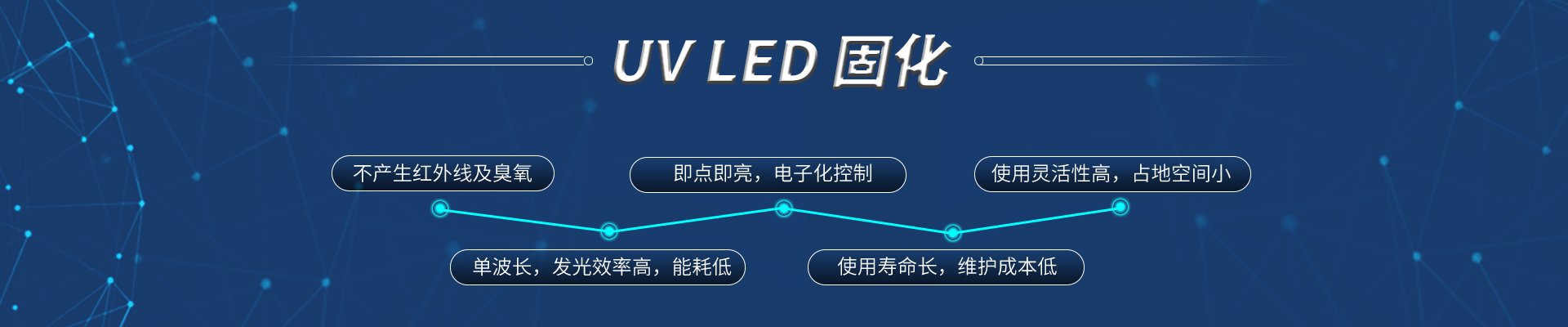
uvled features:
Does not produce infrared rays and ozone
Traditional mercury lamps produce light in a wide range of wavelengths, ranging from infrared light to ultraviolet light. Infrared light has a thermal effect. When it is irradiated onto an object, it can cause most molecules to resonate, thereby generating heat, which can easily cause damage to heat-sensitive substrates. UVLED is a "cold light source" that can effectively avoid adverse effects such as shrinkage and deformation of the substrate due to overheating, and has wider adaptability to materials. The reason why mercury lamps produce ozone is also because the ultraviolet light band they emit is too wide. Ultraviolet light below 240nm can break the double bonds of oxygen molecules, causing the generated O atoms to combine with oxygen to produce ozone. Too high an ozone concentration can cause harm to the human body. The ultraviolet light emitted by uvled for ultraviolet curing has a single wavelength and is ultraviolet light with a longer wavelength. Therefore, ozone will not be generated during the curing process and it can maintain a good working environment. It is safer and more environmentally friendly than traditional mercury lamps.
Single wavelength, high luminous efficiency, low energy consumption
UVLED can efficiently convert electrical energy directly into light energy, and emits single-band ultraviolet light. The light energy is highly concentrated in specific ultraviolet light bands. Currently, the mature application bands in the ultraviolet curing market are 365nm, 385nm, 395nm, and 405nm. In traditional mercury lamps, the hot mercury vapor in the lamp tube emits light after being energized, and the luminous spectrum of the mercury lamp is very wide. Only a small part of the ultraviolet light band that actually plays a curing effect is also low in photoelectric conversion efficiency and high energy consumption.
Instant lighting, electronic control
Mercury lamps need to be preheated before normal operation, and in order to maintain working efficiency and lamp service life, they need to be turned on at all times. UVLED is different. The light can be turned on and off at any time without affecting the service life. It does not require preheating. It can work when the light is turned on. The output energy can also be set according to actual needs. Compared with mercury lamps, it is very energy-saving and easy to control.
Long service life and low maintenance costs
The service life of uvled can reach more than 10,000 hours, which is more than ten times that of traditional mercury lamps. The light decays very slowly, and the service life is not affected by the number of switches. The uvlled light source does not contain mercury and does not have accessories such as lampshades, so it requires little maintenance, reducing maintenance costs.
High flexibility of use and small footprint
UVLED light sources can be divided into point light sources, line light sources, and surface light sources, and the effective illumination range can be customized according to actual use. The light source equipment is small in size, and the irradiation device and related supporting equipment are very compact. It can also be installed on the production line and the parameters can be set well, which can greatly improve production efficiency.
Fast curing
UVLED uses ultraviolet light to cure, which can achieve second-level curing. The curing speed is much faster than traditional curing speed, improving production efficiency.