Indirect pad printing of UV curing machine light solid printingread count [592] release time:2019-12-19 20:54:00
Indirect pad printing refers to a printing method that is not suitable for printing directly on the printing press, but is printed through a transition carrier and then the image is transferred to it. There are many indirect pad printing methods, including Thermal transfer printing, decal printing, pressure transfer, Wet transfer printing and self-adhesive trademark printing, etc., and the printing methods on this transitional transfer body include embossing, silk screen, gravure printing, Lithographic printing etc., since there are front and reverse images during transfer, the image on the transition carrier also has a difference between a front image and a reverse image. At the same time, transfer printing is easy to use and low-cost, and is widely used in transfer printing of product labels, ceramics and glass products, textiles, furniture, building materials and decoration, etc.
(one) UV curing machine Dye-sublimation transfer printing of indirect pad printing fabrics with light-set printing
In addition to printing directly on the surface of textile fiber products using printing and dyeing and screen printing technologies, thermal transfer printing methods are also used, such as sublimation disperse dye transfer, melt transfer, and release transfer. Sublimation transfer is to first print graphics and text on transfer paper (this paper has no affinity with disperse dyes, but only serves as a carrier), and then relies on the action of heat to sublimate the dye and penetrate into the fabric fibers to form a firm coloring, with realistic images and rich layered effects. Thermal transfer printing is mostly used for the transfer of trademarks or graphics on paper-backed fiber products, such as clothing, shoes, hats, and bags.
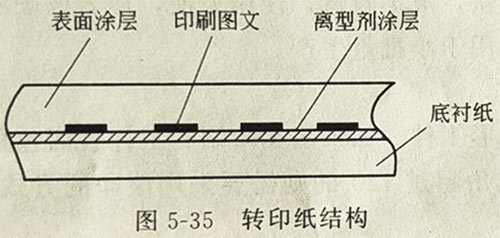
1.UV curing machine The structure of indirect pad printing sublimation transfer paper for light-solid printing
As shown in Figure 5-35, the base material of thermal sublimation transfer is paper (or film), which is coated with a layer of release agent coating. This paper must have a certain adsorption capacity for dye ink, and more importantly, it should have a certain deinking ability. Generally, 60~80g/m2 coated paper or offset paper is used, and it can withstand temperatures of about 150°C. The specific requirements are:
①The paper has high density, smooth surface and appropriate absorbency.
②It has certain strength and toughness and is not easily damaged by high temperature and heavy pressure.
③Requires easy dye transfer.
④Strong water resistance, not easy to shrink.
2. Indirect pad printing thermal transfer ink for UV curing machine light solid printing
Thermal transfer ink is printed by dye sublimation. It is different from conventional ink in that it is mainly composed of disperse dyes and vehicles. The vehicle is mainly a solvent, and the solvents used in different printing methods are different. For gravure printing and silk screen printing, organic solvents or aqueous solvents are used, while for letterpress printing, alcoholic or aqueous solvents are used, and for flat printing, organic solvents are mostly used.
3. Indirect pad printing transfer process of UV curing machine light solid printing
4. Indirect pad printing method of UV curing machine light solid printing
First, choose printing methods such as embossed printing, flat printing, gravure printing and screen printing according to different requirements, then make the corresponding printing plate and use thermal transfer paper on the printing machine for single-color or multi-color printing, and then apply a layer of paint for backup after printing.
There are many fiber products used for sublimation transfer printing. Due to their somewhat different properties, especially for natural fiber fabrics, the fabric generally needs to be resin treated or denatured first. For example, cotton fiber can be treated with acetylation and benzylation to make the natural fiber easy to color the sublimated disperse dye. Its color brightness and fastness are not as good as synthetic fibers. When transferring, for decorative transfer printing on small materials, such as children's clothing, handkerchiefs, skirts, tablecloths, etc., you can cut out the pattern on the transfer paper according to the size of the printed image and text, and then lay the patterned side flat on the front of the fiber item, then use an electric iron to slowly apply back and forth pressure on the paper surface to lift up the transfer paper, and the dye-printed image and text will be firmly attached to the fiber item. For large-format printing materials, thermal transfer conveyor belt machines are used. There are mainly three types:
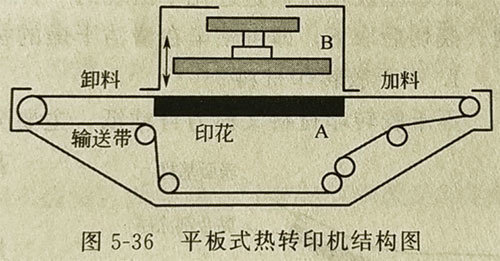
(1) UV curing machine light solid printing indirect pad printing flatbed heat transfer machine is mainly used for clothing printing and decoration printing. As shown in Figure 5-36, during transfer, bottom plate A is heated, the transfer paper is placed on the conveyor belt with the pattern upward, and then the fabric is carefully placed on the transfer paper and sent to the transfer part via the conveyor belt. B is the liner, pressurize it for the required time, that is, the temperature is 180~220℃, and the time is about 15~60s, the transfer can be completed.
(2) Vacuum transfer machines are used for fabric transfer with special requirements, such as thick fabrics, blankets, tapestries, etc. Thermal dye sublimation transfer is generally only suitable for the transfer of synthetic fiber fabrics. It is more difficult to transfer natural fiber textiles. Nowadays, people use a kind of coating ink to form a thin film at high temperature to fix the overall color pattern on the textile. After printing, the fastness is good, the image layer is rich, and the color is bright. The structure of this transfer paper consists of offset paper and a release film. The surface release film has appropriate adhesion to the ink for printing graphics and text, and can easily release the ink layer when heated. The printing method is mainly lithographic printing, using special ink, which is composed of pigments, slurries, adhesives and additives. After printing, in order to transfer the graphics and text smoothly, the graphics and text are coated with a layer of adhesive that can adhere to the fabric. For polyethylene materials, you can also make a printing plate, print a layer of adhesive on the part to be transferred, and use it after drying. When transferring, the printed and adhesive-coated transfer paper is closely connected to the textile on the transfer machine. Under a certain temperature and pressure, the coating ink can be separated from the paper and transferred to the fabric. General household irons can also be used to transfer small patterns.
(3) The continuous cylinder transfer machine is used for transferring fabrics into rolls.
(2) Indirect pad printing of self-adhesive trademark transfer by UV curing machine light-curing printing
Self-adhesive trademark transfer refers to a transfer technology that uses certain pressure and adhesive as transfer conditions to peel off the self-adhesive transfer paper with the image printed on it from the base and directly paste it onto the substrate. It is generally called self-adhesive trademark printing. The printing methods include relief printing, offset printing, flexographic printing, screen printing and gravure printing. In addition to printing, self-adhesive trademark printing also requires post-printing processes such as foil stamping, lamination, die-cutting, creasing, waste discharge, cutting, drying and paper collection. Self-adhesive trademark transfer has the characteristics of flexible adhesion, easy use, strong adhesion, heat resistance, moisture resistance, not easy to age, and does not contaminate goods. It also has a decorative effect and is widely used in household appliances, instruments, machine nameplates, plastic products, furniture and woodware, food packaging, children's toys, office supplies and other commodities.
At present, there are three commonly used printing methods for self-adhesives: offset printing, letterpress printing (including flexo printing) and screen printing. The machine structure is divided into three types of printing: round pressing, round pressing and flat pressing. Products with slightly larger printing layouts, such as posters and trademarks, are usually printed with offset printing presses or letterpress automatic printing machines with a round or round flat structure. The product quality and printing efficiency can achieve relatively satisfactory results. Trademarks and label products with small-format multi-imposition structures that require die-cutting, lamination, and hot stamping are suitable for printing with letterpress self-adhesive label printing machines. This type of machine has the characteristics of integrating the ink distribution and printing mechanisms of both adhesive and convex printing machines into one machine. The material used is roll-type self-adhesive paper, which can realize multi-color printing at one time and complete processes such as foiling, lamination, die-cutting, rewinding scraps, and slitting. It can be printed with metal plates and resin plates. Due to the building block structure, certain functional components can be added or deleted flexibly and conveniently according to the characteristics of the printed parts. The paper feeding structure and paper delivery structure are basically similar to the flexographic printing machine. The difference is that during the entire traveling process, a mechanism that can control the paper step printing is added, which requires strict time control and positioning control to ensure the accuracy of overprinting. Products that require a thick layer of printing ink can be printed with a screen printing machine. The printing ink is bright and bright, making it an ideal printing process for posters and large-area trademarks.
Pressure-sensitive adhesive trademarks are a kind of simple pressure-sensitive transfer paper that has appeared in recent years. The back of the image is coated with adhesive. After printing and die-cutting, it can be removed and can be firmly adhered to the surface of clean and dry items.
1. Self-adhesive transfer material is also called self-adhesive paper, which is mainly divided into self-adhesive paper and self-adhesive film. Its basic structure is composed of surface self-adhesive transfer material base material, adhesive layer and peeling layer, as shown in Figure 5-37.
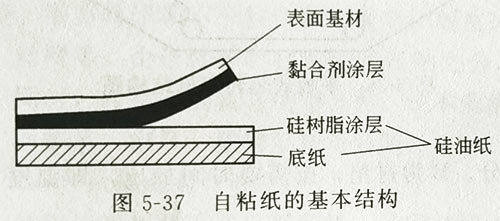
(1) Surface substrate The surface substrate is the carrier of the image, and the adhesive coating materials generally include paper-based printing layers and film printing layers. Currently, the paper-based printing layers commonly used include offset paper, coated paper, various colored glossy and fluorescent papers, aluminum foil and other special papers. Film printing layers include transparent film, translucent film, opaque film, metallized film, special film and other types.
(2) Adhesive layer The adhesive mainly serves to stick to the substrate. According to the chemical characteristics of the adhesive, it can be divided into rubber type, resin type and rubber-resin mixed type; according to the strength of the adhesive's adhesion, it can be divided into strong adhesive type, strong adhesive type and weak adhesive type. The first two types can be stuck on the object all the time and are for one-time use. If the printed image is removed, it will be destroyed. , the latter is a reusable type. It will not damage the goods if it is peeled off after being pasted on the object; according to the characteristics of the surface material, it can be divided into paper self-adhesive, film self-adhesive and special self-adhesive; according to the adhesive coating technology, it can be divided into hot melt self-adhesive, solvent-based self-adhesive and emulsion-based self-adhesive.
(3) Peeling layer (silicone coating) The peeling layer is a layer of silicone oil coated on the paper base or film, which turns the base paper into a smooth surface with very low surface tension, preventing the adhesive from sticking to the base paper, but requires a certain degree of adhesion between the surface base material and the base paper to facilitate printing and die-cutting.
(4) The base layer is used to receive the coating of release agent and support the surface substrate so that it can be die-cut, waste discharged and labeled on the labeling machine smoothly. The base material of self-adhesive paper is usually offset paper or plastic film.
2. Production of printing plates
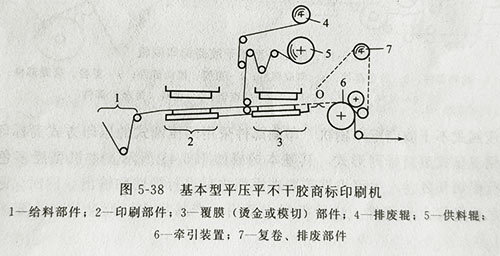
Self-adhesive trademark printing can use screen, letterpress and offset printing, so there are many self-adhesive trademark printing machines with different printing methods. But most of them use letterpress printing. The printing plates are mainly photosensitive resin letterpress plates and flexographic plates. Because it is relatively soft, it can be easily pasted on the printing plate cylinder to make a flexographic plate. In order to adapt to the structural requirements of different self-adhesive trademark printing machines, in addition to the conventional one-color-one-plate, that is, a single-color plate, there is also an integral plate, in which four colors are printed on one printing plate (see Figure 5-38). That is, each color printing plate is made on the same resin plate, but the spacing between each color must be fixed according to the structure of the printing machine. Therefore, special equipment (such as a continuous printing machine) must be used when making the plate to ensure the accuracy of overprinting of each color.
3. The production of hot stamping plates is generally the same as that of photo-etched copper and zinc plates.
4. Production of die-cut version
The die-cut plate is a plate used for shaping technology, which requires the surface paper to be die-cut into shape while the bottom paper remains intact. The die-cut version is made by inlaying a 9mm×0.5mm (width×thickness) knife strip on a 6~8mm thick plywood according to the trademark outline.
5. Printing process
The design of the trademark is different and the printing process is different, but the basic process flow is the same. The general process is as follows:
6. Indirect pad printing self-adhesive trademark printing machine with UV curing machine and light-curing printing
Most self-adhesive trademark printing machines use a multi-process linkage method of web paper. According to the different imprinting methods of the printing unit, self-adhesive trademark printing machines can be divided into three types: flat pressing type, round pressing type and round pressing type. Its structure is basically the same and mainly consists of the following parts.
Printing part: Select according to the number of printing colors, format size, and imprinting method. The running direction of the paper is parallel to the axis of the printing plate cylinder.
Paper feeding section: Inputs the web paper to the printing section.
Coating part: Cover the surface of the printed matter with a layer of film to prevent ink from falling off and increase the brightness of the printed matter. Die-cutting part: Cut the printed matter into half or full cuts into labels of various shapes as needed.
Waste discharge part: the waste paper after die cutting is rolled up.
Hot stamping part: It can be placed before or after printing, depending on the drying condition of the ink.
Slitting part: Placed at the rewinding station, the web can be cut into narrow strips for later use. Rewinding part: Rewind the printed finished product as required.
Drying part: placed after the printing station to quickly dry the ink layer
Cutting part: Cut the printed label into the required size. In addition, the following parts can be optionally selected according to the requirements.
(1) Flat-pressure self-adhesive trademark printing press. This type of printing press can be divided into two types: basic type and standard type. 1) Basic type. The main functions of the basic type are:
①Printing, laminating and collecting
②Printing, hot stamping and collecting;
③Printing, die cutting and collecting
The basic flatbed trademark printing machine mainly consists of feeding parts, printing parts, laminating (hot stamping or die-cutting) parts, feeding (film or gold foil) parts, guide rollers and rewinding and waste discharge parts, as shown in Figure 5-38
Due to the flat-flat embossing method, the web feeding part adopts intermittent motion, so that the substrate can be embossed, laminated, hot stamped, or die-cut simultaneously while the substrate is stationary. This model has a simple structure and is easy to adjust, but its accuracy is not high. It is an entry-level model and is mainly used to print general-grade prints.
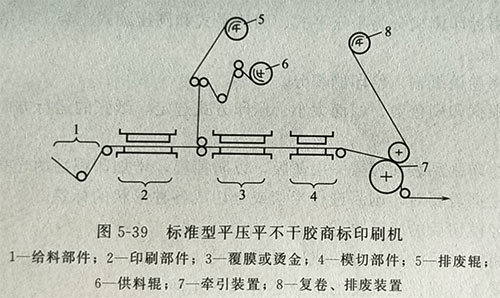
The standard standard flatbed trademark printing machine is continuously improved and perfected on the basis of the basic type. The basic composition is the same as the standard type, except that the printing parts, laminating (or hot stamping) parts and die-cutting parts are set up separately. When the substrate is stationary, embossing, hot stamping and die-cutting are performed simultaneously. At the same time, the hot stamping parts can also be used as lamination. Standard printing machines can use copper-zinc plates or resin plates. They are currently ideal equipment and are mostly used in China.
(2) Circular flattening type self-adhesive trademark printing machine The printing part adopts the circular flattening type embossing method of self-adhesive trademark printing machine. This machine can complete hot stamping, printing (multi-color), die-cutting, laminating, collecting and other processes. Its hot stamping parts, laminating and die-cutting parts are the same as the flat-pressure self-adhesive trademark printing machine, while the printing part adopts the circular-pressure embossing method. The printing plate is an arc-shaped printing plate, which is mounted on a printing plate cylinder. The printing table is fixed during printing, and the printing plate cylinder rotates back and forth once to complete secondary printing or multi-color overprinting. The print quality of this type of machine is higher than that of the flatbed machine, with better reproducibility and resolution of printed images and texts, and it can print mid-range quality prints.
(3) The printing parts of the rotary self-adhesive trademark printing machine adopt the rotary embossing method, and most of the printing parts adopt the satellite roller arrangement. This machine can be used for die-cutting and rewinding after multi-color overprinting and drying, and can also be used for cross-cutting and output after die-cutting as needed. At the same time, the glazing component can also be placed in a color group of the printing component. This type of machine is mainly used in situations where the product is stable, the batch size is large, and high quality is required.
At present, most self-adhesive label printing machines use combined printing components. In addition to completing multi-color overprinting, they also work online with components such as glazing, lamination, die-cutting, and cutting to form a printing and post-press processing production line with a high degree of automation, such as setting up a computer trademark design system and electronic registration and tension control systems.